Understanding the Role of Oracles in Blockchain
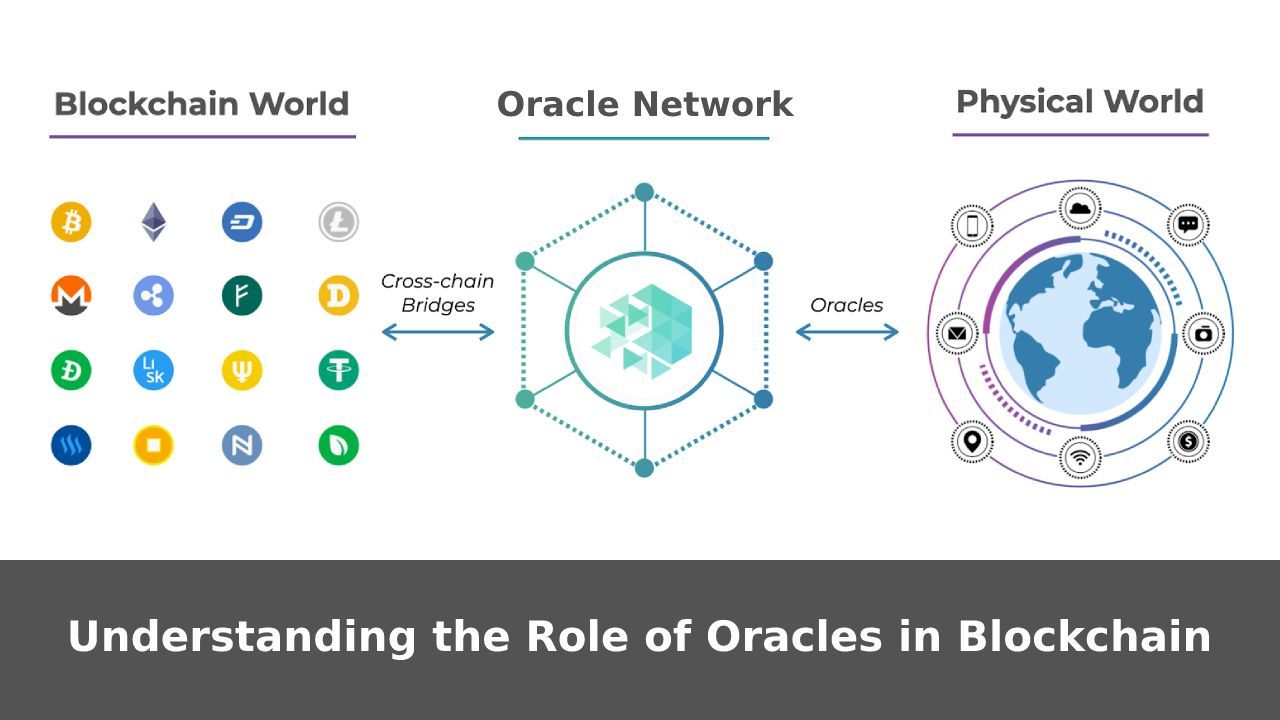
As we delve deeper into the world of blockchain technology, we must understand the importance of certain elements that make the system work seamlessly. One such element is the oracle. In this post, we will explore the role of oracles in blockchain, their types, and their significance in ensuring the security and reliability of the decentralized system.
What are Oracles?
In the context of blockchain, an oracle is a bridge between real-world data and the blockchain network. It is a third-party agent that feeds external data into the blockchain to execute smart contracts. Oracles act as intermediaries that verify, authenticate, and encrypt data, making it viable for use in a trustless system.
Types of Oracles
There are three types of oracles that supplement blockchain technology - software oracles, hardware oracles, and consensus oracles.
- Software Oracles - They are software-based agents that collect and verify data from online sources and transmit it to smart contracts. Examples include APIs, web scraping tools, and data feeds.
- Hardware Oracles - They extract real-world data that is not accessible via online sources, such as temperature, humidity, geographical location, and movement, from IoT devices, sensors, and other hardware. Hardware oracles ensure the authenticity and credibility of hardware-generated data.
- Consensus Oracles - These are decentralized networks of oracles that work in unison to ensure the accuracy and veracity of data. They operate on consensus algorithms that validate information through multiple cross-referencing mechanisms and confirm the data's legitimacy before sending it to the blockchain.
Role of Oracles in Blockchain
Oracles play a crucial role in blockchain technology, as they enable the interaction between the decentralized chain and the real world. Here are some of the key roles that oracles occupy:
Ensuring trustworthiness and reliability of external data
Since smart contracts operate on the information contained in the blockchain, they need external data such as market data, weather patterns, and other real-world events to complete their functions. Oracles provide this raw data to smart contracts in a transparent and secure fashion.
Providing data to smart contracts
Blockchain-based smart contracts can be configured to execute based on external factors, such as stock prices, which are obtained via oracles. Without oracles, such contracts would be impossible to execute automatically.
Verifying off-chain events
Oracles are capable of verifying off-chain events, ensuring that the data transmitted to the smart contract is legitimate. For instance, if a smart contract is designed to release payments to a service provider after a specific task is completed, the oracle will verify that the job is completed before retrieving the payment from the blockchain.
Facilitating inter-blockchain communication
Oracles are necessary to enable the exchange of data between different blockchain networks, allowing them to communicate with one another. This interoperability is essential for creating a globally connected blockchain system.
Use Cases of Oracles in Blockchain
Oracles have several exciting use cases that can improve the efficacy and security of many industries. Here are a few examples:
Insurance
Oracles can provide insurers with accurate, real-time data that can be instantly verified from IoT devices connected to insured assets. This data can be used to automate payments if specific triggers occur, such as theft or damage.
Supply Chain Management
Oracles can provide real-time data from supply chain stakeholders and trigger smart contracts to automate processes such as payments, quality control, and delivery scheduling. This transparency can reduce errors, increase efficiency, and enhance accountability in the supply chain network.
Prediction Markets
Oracles can be used to determine the winner in prediction markets by providing accurate and reliable data about the outcome of events. This reliability ensures that users bet with confidence, and the prediction market operates in a fair and transparent manner.
Common Challenges and Criticisms
Oracles are an essential component of blockchain technology, but they do have their limitations and potential drawbacks. These concerns include:
Centralization concerns
The oracle system can become centralized, leading to potential censorship of data and a single point of failure if not properly managed.
Data reliability and accuracy issues
Oracles work on the assumption that their input data is accurate and reliable. However, if the data is compromised, it can lead to invalid smart contract execution, thereby undermining the trust in the blockchain system.
Security risks
Oracles are an attractive target for hackers, and if compromised, can lead to significant implications for the entire blockchain system.
Future Outlook
As the blockchain technology evolves, advancements in oracle technology are also expected. Some potential developments include:
Potential advancements in oracle technology
Future developments may include improvements to the consensus algorithm, enhancing data processing speed, and data storage capabilities.
Integration of oracles with other emerging technologies
Oracles can be integrated with other emerging technologies such as AI and IoT for improved efficacy, increased automation, and enhanced security.
Conclusion
Oracles are an essential component of blockchain technology as they provide a vital bridge between the decentralized chain and the outside world. They ensure that smart contracts have the real-world data they need to operate efficiently, provide transparency and security, and facilitate the interconnection of different blockchain networks. Oracles are vital in driving blockchain technology beyond its current state and facilitating the realization of its massive potential.